优爱(UA BIOSCIENCE)-重组蛋白专家
优爱,重组蛋白专家
解决方案
技术资源中心
引用文献
IF: 21
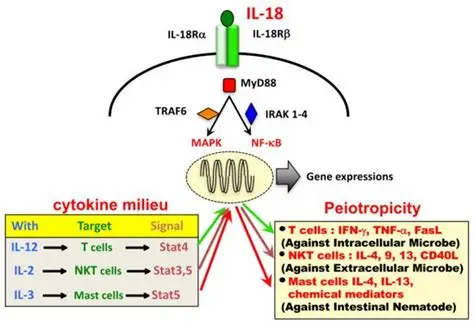
Selective depletion of CCR8+ Treg cells enhances anti-tumor immunity of cytotoxic T cells in lung cancer via dendritic cells
Accumulation of regulatory T (Treg) cells, an immunosuppressive population, limits the efficacy of immunotherapy in NSCLC. C-C motif chemokine receptor 8 (CCR8) is selectively expressed in tumor-infiltrating Treg cells and is, therefore, considered an ideal target.
杂志名称:Journal of Thoracic Oncology
作者:Peixin Chen; Haowei Wang; Zhuoran Tang; Jinpeng Shi; Lei Cheng; Chao Zhao; Xuefei Li; Caicun Zhou
DOI:10.1016/j.jtho.2025.02.029
IF: 15
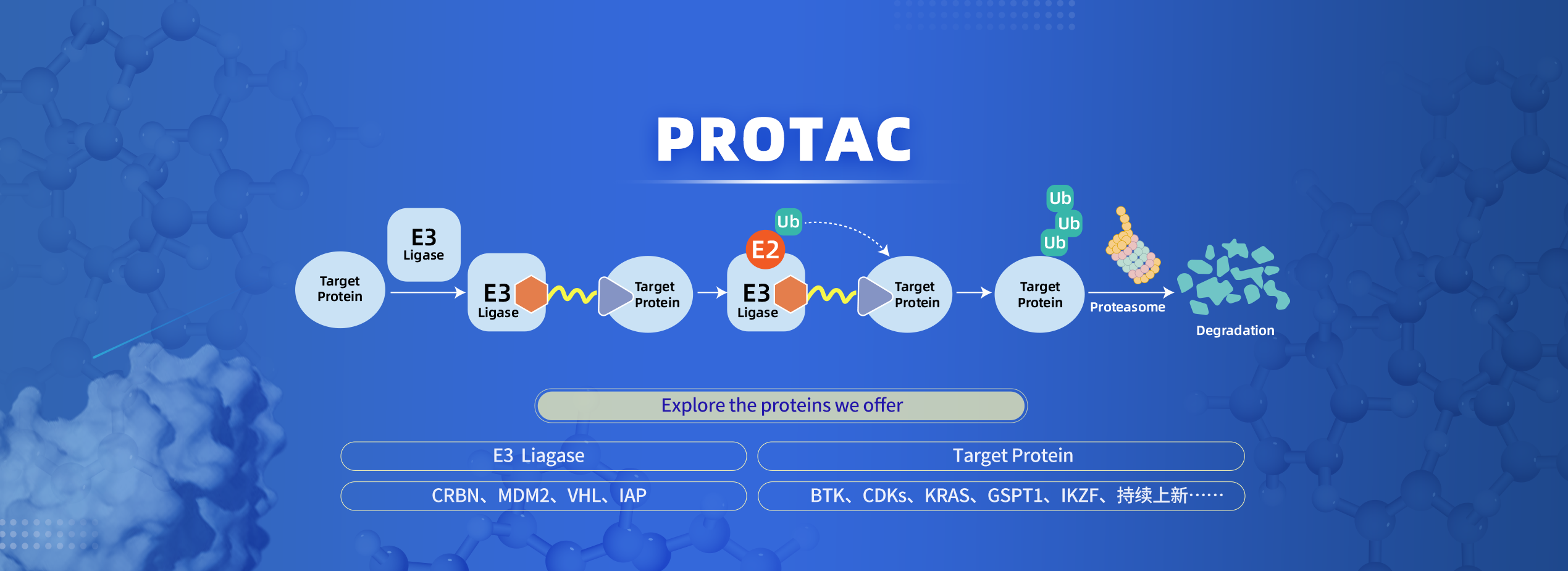
A Dual-Targeted Molecule for Disease-Activatable Proteolysis
Targeting Chimeras and Targeted Radionuclide Therapy of Cancer
Proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) represent a cutting-edge
approach for targeted protein degradation in cancer therapy, yet they face challenges
such as poor pharmacokinetics and specificity issues, leading to undesirable off-target
effects and limited antitumor potency. To address these issues, we introduce dualtargeted unimolecular theranostic probes (e.g., radioactive 177Lu-P-A and its cold
counterpart natLu-P-A) for disease-activatable PROTACs in combination with targeted
radionuclide therapy (TRT) against prostate cancer with high specificity and
effectiveness. The probes achieve a cathepsin B (CTSB)-activatable pro-PROTAC
moiety for precise degradation of bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) and a
prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-targeted 177Lu-based TRT. Owing to the
favorable pharmacokinetics and PSMA-mediated excellent targeting efficiency, the
probe possesses high tumor imaging specificity and accumulation capacity of
therapeutic units for highly effective PROTACs and TRT. In contrast, the free
PROTACs unit (e.g., ARV-771) shows no observable therapeutic effect due to its poor targeting ability. Importantly, the BRD4
proteolysis by PROTAC activation can downregulate radiosensitivity-associated RAD51AP1 expression, synergistically enhancing
the TRT effect and promoting apoptosis after combined therapy compared to individual treatment regimes. Additionally, the probe
demonstrates high renal clearance, underscoring its biosafety for potential clinical translation. This study presents a potential
approach for precise PROTACs combined with TRT for effective tumor therapy.
杂志名称:JACS
作者:Yuan Zhang Wei Gu, Wan Chen, Jieli Zhu, Longfei Fan, Liwen Zhang, Liangyou Zhao, and Qingqing Miao
DOI:doi.org/10.1021/jacs.4c18398
1
查看更多文献